It is a biological system consisting of specific organs and structures involved in bringing air (oxygen) into lungs and removing carbon dioxide from body which is a waste product produced by human body.
respiratory system model labeled
What is respiratory system?
It is a biological system consisting of specific organs and structures involved in bringing air (oxygen) into lungs and removing carbon dioxide from the body, which is a waste product produced by the human body. This all occurs during the process of breathing. To better understand how these processes happen, a respiratory system model labeled can provide clear insights.
Apart from breathing, the respiratory system has other functions as well:
- Filtering/cleaning of air entering the nose
- Humidification and warming of air
- Speech
- Protective cough reflex in case of a foreign body entering airways
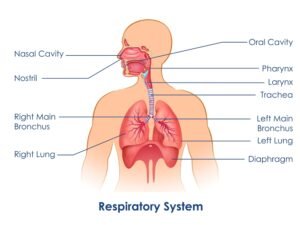
Organs of respiratory system model:
- Nose
- Pharynx
- Larynx
- Trachea
- 2 bronchi
- Bronchioles
- Alveoli
- 2 lungs
The respiratory system is divided into the upper and lower respiratory tract.
Upper Respiratory Tract: It includes the nose, pharynx, and larynx. The role of the upper respiratory tract is to draw air inside and then push it down the lower respiratory tract during the process of inhalation (breathing in) and expel carbon dioxide coming from the lower respiratory tract out to the environment during exhalation (breathing out). A respiratory system model labeled will clearly show how air moves through these structures.
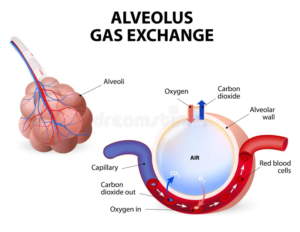
Lower Respiratory Tract: It includes the trachea, bronchi, bronchioles, alveoli, and lungs. The trachea, bronchi, and bronchioles transport air to alveoli, where gas exchange takes place. During the process of gas exchange in the alveoli, oxygen from the air in the alveoli enters blood vessels called capillaries surrounding the alveoli, and carbon dioxide, which is the waste product in blood, goes into the alveoli from capillaries.
The trachea divides into the right and left bronchi. Each bronchus enters the lung and divides into smaller airways called bronchioles inside the lung. Bronchioles then end up in alveoli. When using a respiratory system model labeled, you can clearly identify where the trachea divides and how the bronchi and bronchioles look as they branch into smaller structures.
Pharynx
Pharynx is part behind mouth and nasal cavity and above the esophagus (food pipe) and the larynx (voice box).
Pharynx is divided into 3 parts:
- Nasopharynx , part behind nose
- Oropharynx , part behind oral cavity/mouth, it continues into esophagus (food pipe).
- Laryngopharynx / Hypopharynx , part behind larynx
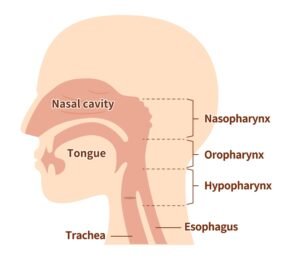
Larynx
The larynx, also called the voice box, extends from the root of the tongue and lies in front of the laryngopharynx/hypopharynx. It continues into the trachea. When using a respiratory system model labeled, you can identify the larynx as the voice box, which helps in speech production.
Trachea
The trachea or windpipe is a continuation of the larynx and extends downwards until it divides. The trachea is 100 mm long and ranges from 15 mm to 20 mm in diameter. The trachea divides at the level of the fourth vertebral body into right and left main bronchi. The right main bronchus is ∼25 mm long (7–10 mm in diameter). The right main bronchus is wider, shorter, and more vertical than the left main bronchus, and hence foreign bodies tend to lodge more frequently into the right main bronchus. The left main bronchus is longer, measuring ∼40 mm in length (7–10 mm in diameter). The respiratory system model labeled will clearly show how the trachea divides and the differences between the right and left bronchi.
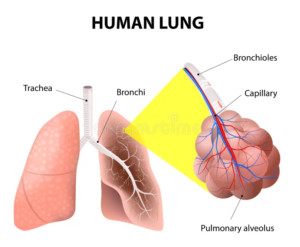
Bronchus, bronchioles and alveoli
The main bronchus on each side branches out and becomes narrower as they approach the lung, forming secondary and tertiary bronchi. Tertiary bronchi divide further to form smaller airways called bronchioles. Bronchioles divide into terminal bronchioles, then respiratory bronchioles, which in turn evolve into alveoli, which is the site of gas exchange.
Alveoli form bunches called alveolar sacs. Alveoli are surrounded by small blood vessels called capillaries. Oxygen from alveoli during inhalation enters capillaries, and carbon dioxide from blood is released into alveoli, from where it goes out of the body during exhalation, passing through all the above-mentioned structures. A respiratory system model labeled is essential to see how the bronchioles connect to the alveoli, where oxygen and carbon dioxide are exchanged.
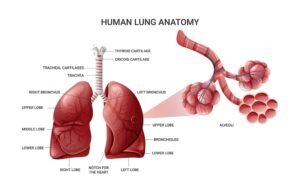
Respiratory System Model Labeled
This model helps to visualize how air flows through the body and the role of each part of the respiratory system. With a respiratory system model labeled, you can see exactly where each part of the system is located and how they function together in the process of breathing and gas exchange. Understanding the respiratory system is crucial to comprehending how oxygen is brought into the body and how carbon dioxide is expelled during normal breathing and other respiratory functions.
By viewing a respiratory system model labeled, you gain a better understanding of how each organ works within the larger system. From the nasal cavity to the alveoli, the detailed labeling of the respiratory model aids in learning how gases are exchanged, which is vital for maintaining proper function within the body.
Human Lung Functioning Diagram
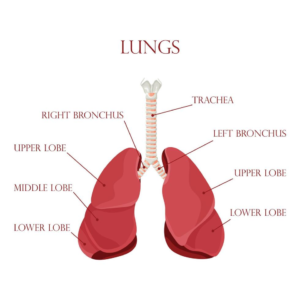
Lungs:
- There are two lungs
- The right lung consists of upper, middle and lower lobes
- The left lung is composed of an upper and lower lobe
- The lungs are covered by a fine membrane known as the pleura. The parietal pleura is the outer layer and the visceral pleura is adherent to the lungs. These two layers are in continuity with each other and there is a very fine space between the two called the pleural cavity.